What is a Pre Fabricated Home and How Does It Work?
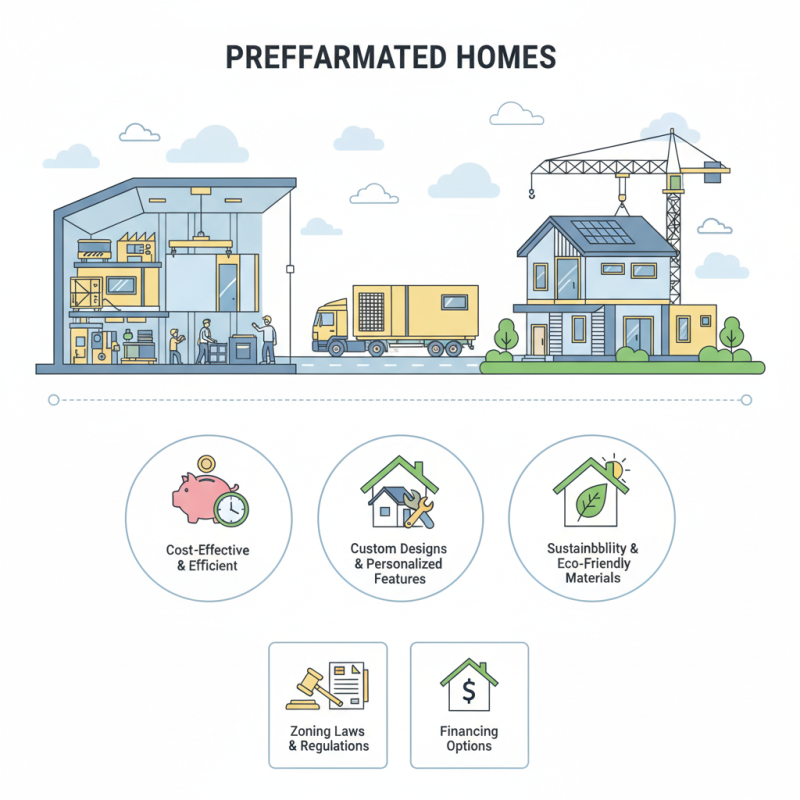
Pre fabricated homes are gaining popularity in today's housing market. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, they account for about 3% of new single-family homes. This growth shows how individuals and families are looking for cost-effective and efficient housing solutions. Pre fabricated homes are built in factories and assembled on-site, offering speed and convenience.
These homes often reduce construction time by 30-50%. Many homeowners enjoy custom designs and personalized features. However, perceptions of quality can be a concern, as some may view pre fabricated homes as less durable compared to traditional houses. The potential for sustainability is significant, too; many modular builders are focusing on eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient designs.
Yet, challenges exist. Zoning laws and land regulations can complicate the placement of pre fabricated homes. Financing options may also be limited, affecting buyers' decisions. As this market continues to evolve, understanding its complexities is crucial for potential homeowners.
What is a Prefabricated Home?
Prefabricated homes, often called prefab homes, are structures built off-site. They are manufactured in a factory and then transported to their final location. This process allows for better quality control and efficiency.
Prefab homes can be more affordable than traditional homes because of reduced labor costs and shorter construction times. These homes come in various designs and sizes. Some are small cabins, while others can be large family houses. Most are customizable to fit individual needs. However, customization can sometimes complicate the process. It may take longer than expected to finalize designs. Not all local building codes may accommodate prefab construction.
Buying a prefab home may require some reflection. While the convenience is appealing, buyers should evaluate their specific needs. For instance, consider the site preparation necessary before installation. Accessing utilities can also pose challenges. Researching local regulations is vital to avoid surprises. Despite the potential drawbacks, many find prefab homes a practical choice in today’s housing market.
Types of Prefabricated Homes: Modular, Panelized, and Manufactured

Prefabricated homes have gained popularity in recent years. They offer a quick and efficient building process. Three main types exist: modular, panelized, and manufactured homes. Each has unique characteristics that cater to different needs and preferences.
Modular homes are built in sections at a factory. These sections are then transported to the building site. According to recent industry reports, modular homes can be up to 20% more energy-efficient than traditional builds. This makes them an appealing choice for environmentally conscious buyers. Panelized homes use large panels that are assembled on-site. This method reduces labor costs and shortens construction time. Lastly, manufactured homes are built entirely in a factory. They are often the most affordable option, appealing to budget-conscious consumers.
**Tip:** When considering prefabricated homes, assess your space needs and budget carefully. Ensure the type you choose aligns with your lifestyle.
While prefabricated homes have many benefits, they may also present challenges. Limited customization options can be a drawback for some. It's essential to understand local zoning laws, as they can impact the home type you can build.
**Tip:** Research local regulations thoroughly before making a decision. This could save you time and resources.
The Construction Process of Prefabricated Homes
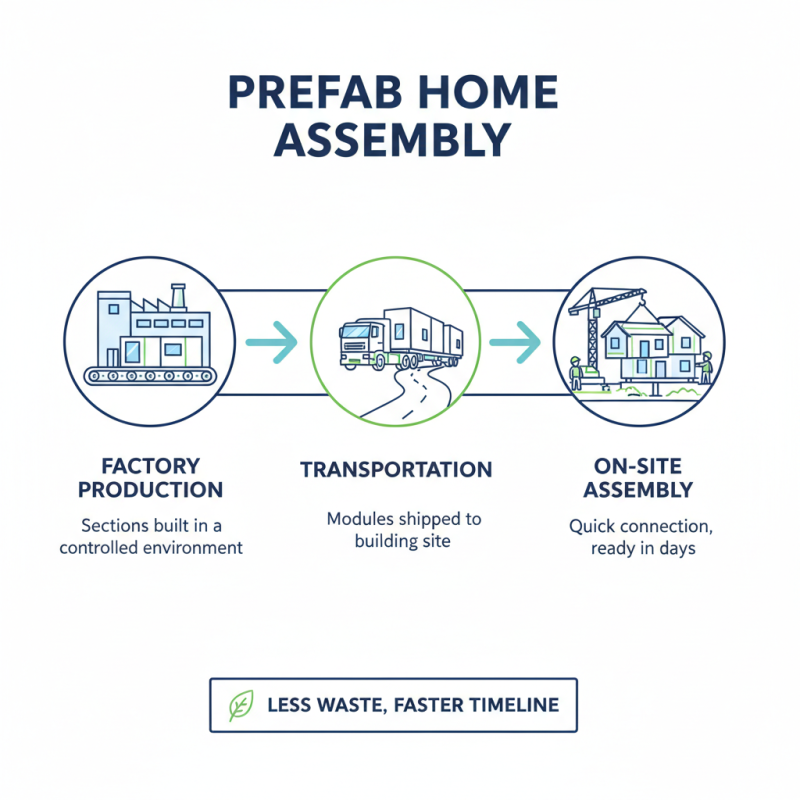
The construction process of prefabricated homes is both innovative and efficient. These homes are built in sections at a factory, then transported to the site for assembly. This method helps reduce waste and often speeds up the overall timeline. Once on-site, these sections are connected, usually within a few days.
One important aspect is ensuring proper placement of the foundation. A sturdy foundation is vital for stability. Misalignment can lead to significant issues later on. Workers check the level and adjust as needed. This part of the process cannot be rushed.
Tips: Always double-check local building codes. Different areas have varying requirements that must be met. Also, consider your long-term home design. Some prefabricated homes can be hard to modify later. Think about your family's needs now and in the future. Be prepared for unexpected hiccups during assembly. Weather delays or material shortages can occur. Stay flexible and adapt your plans as needed. Being patient will pay off.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Prefabricated Homes
Prefabricated homes are gaining popularity, but they come with both advantages and disadvantages. One major benefit is the cost-effectiveness. Building materials are manufactured in a factory, reducing waste and overall costs. This makes housing more affordable for many families. Additionally, construction time is significantly shorter. Homes can be assembled quickly, sometimes in just a few weeks.
On the downside, customization options may be limited. If you have specific design preferences, a prefabricated home might not fully meet your needs. Some people find they feel less attached to a factory-built structure. There can also be quality concerns. While many manufacturers produce high-quality homes, others may cut corners to save costs. This variability can be troubling for potential homeowners, who want assurance about what they are investing in.
The location can pose challenges as well. Not all areas can accommodate prefabricated homes due to zoning laws. Finding land that meets these requirements can be difficult. Some buyers may experience frustration with the logistics of transportation and assembly. Thus, despite the appeal of affordable and quick housing options, the journey may require careful consideration and planning.
Financing and Buying a Prefabricated Home: Key Considerations
Financing a prefabricated home is quite different from traditional homes. A report from the National Association of Home Builders indicates that prefabricated homes can cost 10-20% less than site-built homes. This lower price can make them an attractive option for buyers. However, buyers should be aware of hidden costs. Land preparation, transportation, and assembly can add significant expenses.
Mortgage options for prefabricated homes often vary. Some lenders specialize in prefabs, while others may not finance them at all. According to a survey by the Mortgage Bankers Association, almost 25% of lenders require more documentation for prefabricated homes. This can delay the buying process. If plans fall through, buyers may feel disheartened.
Understanding zoning laws is essential before purchasing. Local regulations can affect where you place your home. A report from the U.S. Census Bureau shows that about 15% of buyers encounter unexpected zoning issues. Frustration can mount if these hurdles arise after you've invested time and money. Community restrictions also play a role. Some neighborhoods have specific guidelines for prefabricated homes, limiting your choices.
Related Posts
-

Why Pre Manufactured Homes Are the Best Choice for Affordable Housing Solutions
-

Exploring the Future: Sustainable Living with Innovative Prefab Homes
-

Exploring the Benefits of Choosing Pre Manufactured Homes for Modern Living
-

2025 Top 5 Modern Modular Homes Revolutionizing Sustainable Living and Design
-

10 Best Prefabricated Homes for Your Dream Living Space
-

2025 Top 5 Trends in Prefabricated Small Homes for Sustainable Living
